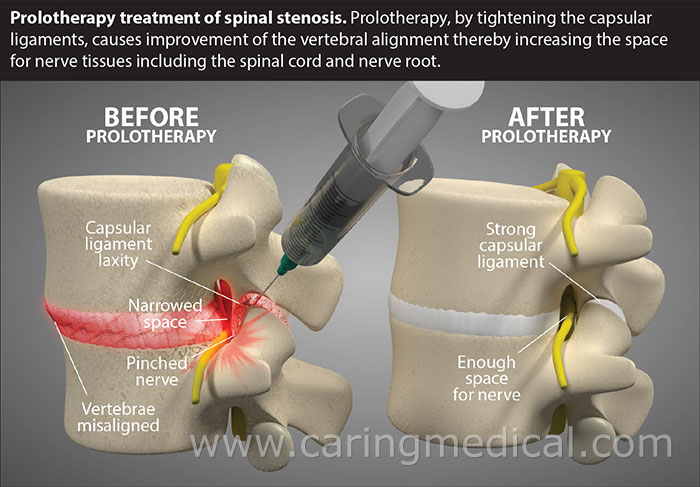
Lumbar spinal stenosis, a condition characterized by the narrowing of the spinal canal in the lower back, often leads to significant discomfort and disability, especially in individuals over 50 years of age. This narrowing, caused by bone or tissue growth, exerts pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. The initial approach to managing this condition usually involves conservative, nonsurgical treatments. These may include physical therapy, NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs), or electrical spinal cord stimulation.
Physical therapy is a cornerstone in the management of lumbar spinal stenosis. It aims to strengthen the back muscles, enhance flexibility, and improve overall spinal function. Pain medication, particularly NSAIDs, plays a critical role in alleviating inflammation and pain associated with this condition. In some cases, electrical spinal cord stimulation may be employed as an alternative or adjunct therapy, offering pain relief through electrical impulses.
However, if these conservative measures fail to provide adequate relief, surgical intervention might be necessary. Laminotomy, a common surgical procedure for lumbar spinal stenosis and herniated disks, is considered when symptoms like numbness, weakness, and balance issues persist despite conservative treatments. In more severe cases, especially when abnormal movement of the spine is suspected, a laminectomy and fusion with instrumentation may be performed. This could be done through traditional or minimally invasive spine surgery techniques.
For individuals experiencing early symptoms of stenosis, simple activity modification and anti-inflammatory medications might suffice. When symptoms escalate, epidural steroid injections are another treatment option to consider.
To learn more about the various treatments for lumbar spinal stenosis, visit Hospital for Special Surgery, Ohio State Wexner Medical Center, Harvard Health, Columbia Neurosurgery, UTHealth Neurosciences, Hospital for Special Surgery, and University of Virginia Neurosurgery for comprehensive information.