Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is an inflammation of the mucous membranes lining the sinuses, leading to various symptoms. This condition often results in the production of thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain. Other common symptoms of sinusitis include fever, headaches, a diminished sense of smell, sore throat, and a sensation of phlegm draining.
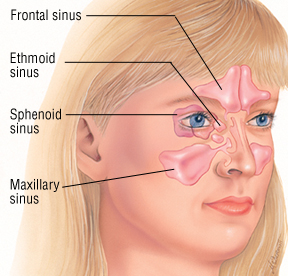
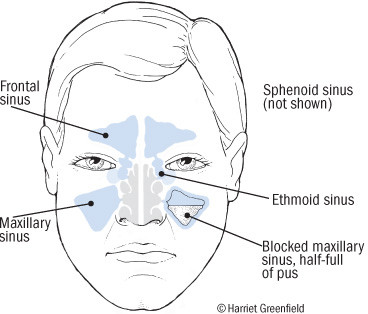
Different types of sinusitis can cause pain in various areas of the face, depending on the affected sinus. Painful pressure is a hallmark symptom of a sinus infection. The location of this pain can vary: frontal sinusitis causes pain in the forehead; maxillary sinusitis leads to pain over the cheek or in the upper jaw and teeth; pain behind the eyes might indicate ethmoid or sphenoid sinusitis; and sphenoid sinusitis can cause pain at the top of the head.
Sphenoid sinusitis, which occurs behind the eyes, can lead to earaches, neck pain, or headaches at the top of the head or deep behind the forehead. Maxillary sinusitis, occurring behind the cheeks, can cause pain in the cheeks, under the eyes, or in the upper teeth and jaw. Sinus infections are also more likely to cause a green nasal discharge, fever, and facial pain.
When it comes to managing sinusitis, observation and patience are often recommended, especially in cases where the symptoms are severe. Sharp pain in the cheeks or teeth accompanied by fever can be alarming signs of a bacterial sinus infection. If cold-like symptoms recede but then return with increased severity, including pain and fever, antibiotics may be considered. However, the effectiveness of antibiotics can be limited in treating sinusitis.
Sinus infection symptoms can follow a different path than common colds. Most cases start as a common cold, and symptoms typically resolve in 7 to 10 days. A sinus infection can develop following an upper respiratory infection (URI) or common cold that doesn’t seem to go away. The URI can cause inflammation of the nasal passages, leading to obstruction of the sinus openings, which then results in repeated cycles of infection and inflammation in the sinuses.
Acute sinusitis refers to a viral infection lasting 7 to 10 days, while a bacterial infection can last up to 4 weeks. Chronic sinusitis, where symptoms persist for 12 weeks or more, can be particularly challenging, with inflammation lasting for months or even years. Factors that can exacerbate chronic sinusitis include common colds, viral infections, a compromised immune system, nasal allergies, nasal polyps, septal deviations, and enlarged vascular structures in the nose.
For more detailed information on sinusitis, its symptoms, and treatment options, visit the comprehensive resources provided by Harvard Health and Stanford Medicine.