Autoimmune disorders that specifically target the muscles, joints, and nerves can significantly impact an individual’s daily life, with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and multiple sclerosis (MS) being prime examples. These conditions can lead to severe joint damage, resulting in chronic pain, impaired balance, and joint deformity. Additionally, RA has the potential to affect various organs, including the lungs, heart, and eyes. There are two main types of RA: seropositive and seronegative.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a type of autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in the joints, leading to inflammation and pain. This condition can also affect other parts of the body, including the heart, lungs, nerves, eyes, and skin. Women are predominantly affected, with 78% of autoimmune disease cases being female. Other risk factors include obesity and certain infections.
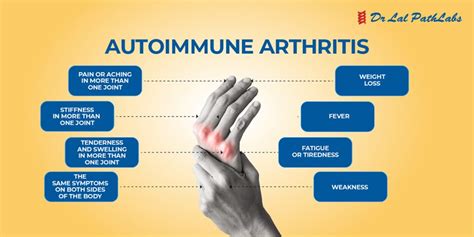
Symptoms of autoimmune diseases vary depending on the type of disease. For diseases affecting the joints and muscles, common symptoms include muscle aches, joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and muscle weakness. Inflammatory responses are also a common occurrence.
Autoimmune arthritis encompasses a range of arthritis types where the body’s immune system attacks itself. The most prevalent form is rheumatoid arthritis (RA), characterized by the immune system targeting the body’s joints. Common causes of joint pain extend beyond autoimmune diseases and can include conditions such as Adult Still’s disease, ankylosing spondylitis, bone cancer, broken bones, bursitis, and more.
Rheumatoid arthritis is classified as an autoimmune disorder, leading to inflammation in and around the joints. Treatment options are available, with joint replacement surgery being a viable option for those with significant joint damage. The surgery aims to alleviate pain and enhance joint function.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is highlighted as an autoimmune and inflammatory disease by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), noting that it predominantly affects the joints in the hands, wrists, and knees. RA can lead to painful swelling and can affect numerous joints simultaneously.
Learn more about autoimmune disorders affecting the joints and nerves from Everyday Health, explore types, symptoms, and diagnosis of autoimmune arthritis at Verywell Health, and understand rheumatoid arthritis better with information from Mayo Clinic. Additional resources can be found at the Cleveland Clinic, Medical News Today, and the Johns Hopkins Medicine websites. To learn more about joint pain causes, visit Mayo Clinic. For information on rheumatoid arthritis from a governmental perspective, the CDC provides a comprehensive overview.


