Rheumatic diseases encompass a variety of conditions characterized by inflammation, pain, and degeneration of connective tissues and joints. Types of rheumatic diseases include, but are not limited to, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. These diseases have complex symptoms and causes, making them challenging to diagnose and treat.
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that can cause inflammation, pain, and damage to various parts of the body. Early diagnosis is crucial in preventing more serious complications and mitigating severe symptoms. Blood tests for markers of autoimmune diseases, such as antinuclear antibody (ANA) and rheumatoid factor, along with a complete blood count (CBC), can aid in the diagnosis and management of these conditions.
Rheumatic Diseases: Types, Symptoms, and Causes – Healthline provides an extensive overview of the types, symptoms, and causes of rheumatic diseases, contributing to a better understanding of these complex conditions.
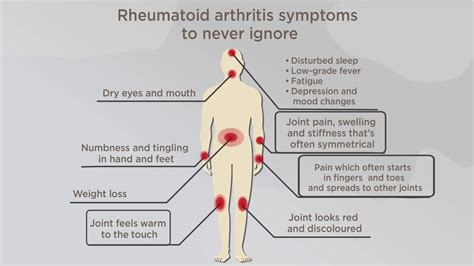
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, leading to inflammation, pain, and eventual joint damage. The disease can also cause a variety of other symptoms, including weakness, fever, and fatigue. Adopting suitable sleep positions and incorporating specific tips can significantly improve rest and overall well-being for individuals with RA.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Sleep Positions and Tips for a Better Rest – Healthline offers valuable advice for people with rheumatoid arthritis to achieve better sleep and manage their symptoms more effectively.
The prevalence of systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARDs) has been noted to be accompanied by a variety of neuropsychiatric symptoms. A study highlighted a discrepancy between the self-reported symptoms of patients and the estimations made by clinicians, underscoring the need for improved awareness and understanding of these symptoms for better patient care.
Clinicians May Underestimate Neuropsychiatric Symptoms Among Patients – This article discusses the underreporting of neuropsychiatric symptoms in patients with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases, emphasizing the need for enhanced clinical attention.
The global battle against rheumatoid arthritis continues as the disease remains a pervasive and unpredictable enemy. Affecting individuals regardless of age or circumstance, rheumatoid arthritis necessitates ongoing research and awareness efforts to better understand, treat, and ultimately cure this debilitating condition.
An Invisible Enemy: The Global Battle Against Rheumatoid Arthritis – MSN discusses the ongoing challenges and global impact of rheumatoid arthritis, highlighting the need for continued research and awareness.
Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis represents a subtype of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, characterized by its limited joint involvement. Proper management and treatment strategies are crucial for alleviating symptoms and improving the quality of life for affected children.
Pauciarticular Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms & Management – HealthCentral provides insight into the symptoms and management strategies for pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, aiding in the care of affected children.
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought about an increased awareness of the potential link between viral infections and the onset of autoimmune and autoinflammatory disorders. Research has indicated a heightened risk of developing these conditions post-COVID-19 infection, adding another layer of complexity to the understanding of autoimmune diseases.
Research: Autoimmune Autoinflammatory Disorders Rise After COVID – WebMD explores the correlation between COVID-19 and an increased risk of autoimmune and autoinflammatory disorders, shedding light on the potential long-term impacts of the virus.
October 9, 2023, marks a significant date in the ongoing research into autoimmune diseases and their potential links to COVID-19. A new study has shed light on the increased risk of autoimmune disorders affecting various parts of the body, from hair follicles and blood vessels to joints and lungs, post-COVID-19 infection. This highlights the critical need for ongoing research and vigilance in monitoring and managing autoimmune conditions in the context of the global pandemic.
COVID-19 Could Increase the Risk of Autoimmune Disorders – Everyday Health delves into the potential connections between COVID-19 and an increased risk of developing autoimmune disorders, underscoring the importance of awareness and research in this area.


